What is the Spinal Cord and What Does it Do?
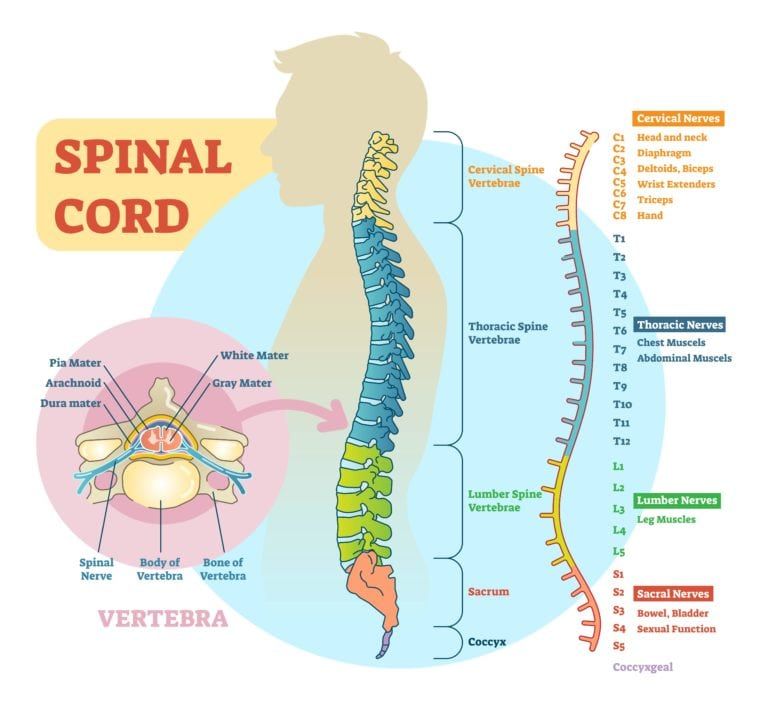
The spinal cord is a long, tubular bundle of nerves that acts as your primary support system, connecting various parts of the skeleton. It is a part of the central nervous system and is also responsible for relaying information from the brain to the other parts of the body. The spine has 26 vertebrae and is divided into five sections from top to bottom including seven cervical vertebrae, twelve thoracic vertebrae, five lumbar vertebrae, one sacrum made of five fused sacral vertebrae, and one tailbone made up of four fused coccygeal vertebrae. The different sections of the spine are all composed slightly differently and have different levels of flexibility. The cervical vertebrae, or section that makes up the neck, are the most flexible vertebrae of the spine. Also, the amount of weight carried by each vertebrae increases the lower the vertebrae sits, meaning lower vertebrae are much larger.
One of the spinal cords major functions is to serve as a communication pathway between the brain and rest of the body. The spinal cord can both send and receive information about the body as well as the external environment and can help regulate vital bodily functions such as heart rate, temperature, homeostasis, and breathing. Your spinal cord is actually responsible for signaling your sweat glands to produce sweat and cool the body. In certain instances of spinal cord injury, individuals can lose the ability to sweat if this connection is interrupted.
Part of acting as the communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body is coordinating reflexes. Reflexes are involuntary responses to outside stimuli in an attempt to protect the body from harm. However, during a reflexive response, the spinal cord often initiates the response separately from the brain. This means you could react to something without knowing why you are reacting to it because your spinal cord caused the reaction and your brain has not yet processed the physical sensation.
The reason the spinal cord is able to function in this way is because it contains the same gray and white matter as does the brain. Gray matter is composed of neurons that pertain to motor or sensory function and is located on the inside of the cord, while white matter is made up of communication pathways.
Since the spinal cord acts as a messenger and stimulates so many vital functions in the body, damage to the spinal cord can cause a range of problems. Generally trauma injuries to the spinal cord only affect the areas below the site of the injury, meaning the higher up the injury, the more risk there is for potential complications. One of the main reasons spinal cord injuries are so serious is because the cells within the spine are so specialized they cannot replicate themselves to repair whatever damage has been done. This means that recovering from a spinal injury is much harder than recovering from any other type of injury.


Recent Comments